The life of the sidewall blocks in the float glass furnace is one of the important factors that determine the life of the glass furnace. However, the use of fused cast AZS blocks on the side wall is very easy to produce cracks when baking the glass furnace, which seriously affects the service life of the glass furnace and the quality of the glass, especially in recent years, the use of the side wall knife blocks has led to the phenomenon of the explosion of the sidewall blocks is more common, and the degree of explosion is more serious. This article combines the actual situation of the baking furnace, analyze how to avoid the problem of sidewall block cracking.
Fused cast AZS blocks are commonly used in the side wall of float glass melting furnaces, and fused cast AZS blocks with zircon content of 33%, 36% and 41% are the most commonly used. In terms of block shape, it is divided into straight type, beam type and knife handle type. According to the current use of sidewall blocks in China, no matter which variety or any kind of casting method of straight blocks, the service life is only 5 ~ 6 years after passing through a side wall binding blocks, which is difficult to extend. Therefore, by the late 90s of the 20th centuries, knife blocks were gradually used by some domestic manufacturers. Judging from the current use, the knife handle block is obviously better than the straight block, which not only provides convenience for binding blocks, but also can tie the blocks twice, which obviously prolongs the service life of the sidewall blocks. Therefore, in the 21st century, knife handle type sidewall blocks have been widely used in float melting furnaces. Especially in the past two years, in order to meet the needs of longer glass furnace age, 41# AZS knife handle blocks have been used in many float melting furnaces. However, due to the special type of knife handle block and the thermal characteristics of fused cast AZS block itself, it is easy to crack or even explode when baking the glass furnace. In particular, fused cast AZS 41# knife handle blocks are more likely to burst. If the method used in the glass furnace is improper or there is an accident such as a power outage during the glass furnace, 100% of the sidewall tiles will burst, which will seriously affect the service life and shorten the glass furnace age. Therefore, it is crucial to minimize the explosion of sidewall tiles when baking the glass furnace.
In order to reduce the explosion of sidewall blocks, the glass refractory industry at home and abroad has carried out a lot of research more than ten years ago, especially the thermal stress and other characteristics of refractory materials have been deeply analyzed, and have achieved certain results, the following combined with the actual situation of a company‘s 500 t / d melting glass furnace baking glass furnace on the explosion factors and countermeasures of the sidewall blocks are analyzed as follows.
1. Reasonable heating rate
From the point of view of the fused cast AZS block itself, the heating rate is controlled below 15 °C / h and will not produce cracks, from the perspective of the heating curve of each float melting furnace, the heating rate will not exceed 15 °C / h, but in the actual heating operation, there is often a sudden rise or fall of the local temperature in a short period of time, such as the oil gun is extinguished and failed to ignite in time, which will cause the temperature of the inner surface of the sidewall block to drop significantly. For example, when the oil quantity is not adjusted carefully, the oil volume of a single gun will increase suddenly, resulting in the local temperature rising too fast, etc., which will lead to the explosion of the sidewall blocks, so the above situations should be avoided as much as possible in actual operation.
2. Reasonable sidewall cooling fan on time
At this point, there are currently two different practices, one is to the French company SEFPRO as the representative of the practice, that is, the sidewall cooling fan in the furnace temperature rises to 500 ° C below the opening, and control the air volume, the domestic use of this method is more common;
The second is the practice represented by Japan‘s AGC, that is, when the temperature in the glass furnace reaches more than 1400 °C, the fan is turned on when the glass phase in the sidewall block is precipitated, and the stress generated after the fan is turned on will be absorbed by the glass phase. This method requires that when the fan is opened, the air volume should be small enough and can be accurately controlled, and the cooling fan should be preferably a frequency conversion fan.


3. Reasonable sidewall insulation
In the baking furnace method with the blower on below 500 °C, no insulation is required on the brick-bind portion of the sidewall; in the baking furnace method with the blower on above 1 400 °C, temporary insulation is added to the brick-bind portion of the sidewall (Below).
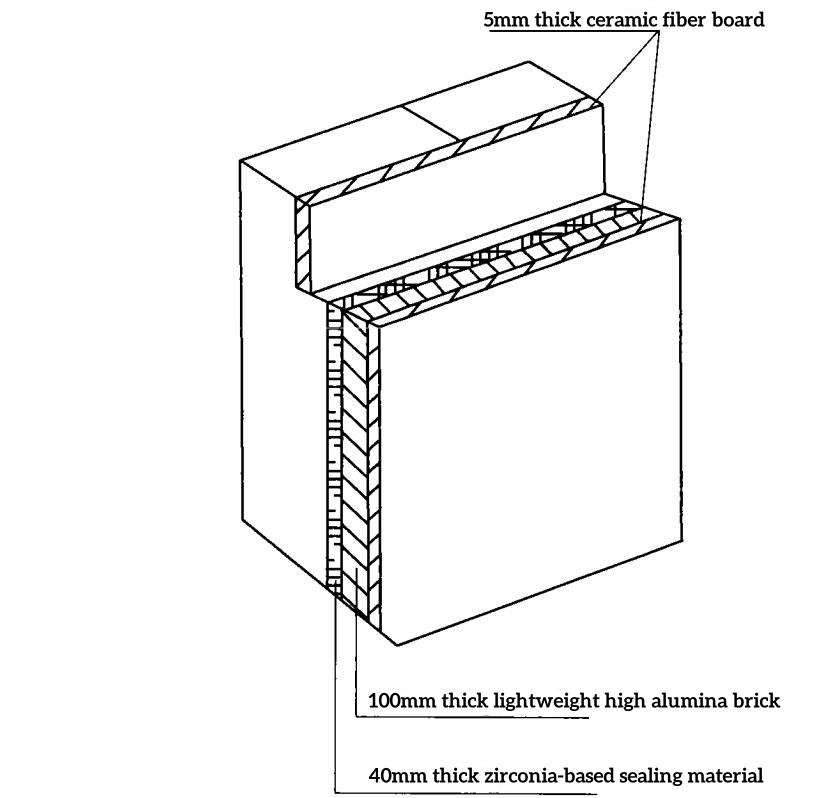
In view of the above factors affecting the explosion of sidewall blocks, the following measures were formulated in the formulation of a company‘s 500 t/d melting glass furnace baking glass furnace plan, combined with the specific situation and actual operation experience of our company and the actual situation of the glass furnace sidewall blocks using fused cast AZS 41# knife handle blocks.
(1) A reasonable heating curve was formulated, and the heating rate was strictly controlled, especially the sudden rise of glass furnace temperature after excessive fire, and the actual heating curve parameters are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Parameters of the actual heating curve.
|
Temperature rise range/°C |
Temperature rise rate/°C - h-1 |
Time spent/h |
|
10~100 |
3 |
30 |
|
100~350 |
1 |
250 |
|
350~600 |
3 |
83.3 |
|
600-850 |
6 |
41.7 |
|
excessive fire |
|
|
|
850-1 200 |
10 |
35 |
|
1 200~1 450 |
13 |
19.2 |
|
|
|
459.2 (19 days 3.2 hours) |
From the above data, it can be seen that from 600 °C to 1450 °C, the maximum heating rate is 13 °C/h, which is controlled within 15 °C/h, and by controlling the number of heavy oil gun ignition during the fire, the glass furnace temperature only rises by 15 °C in a short period of time after the fire, which effectively controls the explosion of the sidewall blocks.
(2) Combined with the actual situation, formulate the cooling plan of the sidewall. In the history of that company, the method of opening the sidewall fan at low temperature has been used in the baking glass furnace, and some experience has been accumulated in the baking glass furnace for many times. So the sidewall cooling fan is still started at low temperature in this program. This is because the air volume control regulates the butterfly valve with 10 % ventilation even when fully closed. Therefore, in terms of controlling the air volume, that company has adopted a relatively earthy but very applicable method, that is, using corrugated paper to block the filter screen of the air inlet of the fan.
Tear off a part of the corrugated paper every once in a while, to control the air intake and control the cooling air volume of the sidewall. This method can control the air volume to a relatively small extent. Practice has proved that in the case of not using a variable frequency fan, this method is feasible and convenient, and can effectively control the cold impact of a large amount of cooling air on the sidewall blocks when the fan is turned on.


(3)According to the opening plan of the cooling fan on the sidewall, in this baking glass furnace, the upper part of the sidewall is not temporarily insulated.
In addition, in the heating operation of the baking glass furnace, the operator is required to operate carefully and watch the burner gun. At low temperatures, if the oil gun is extinguished, it should be ignited in time to avoid the temperature drop in the glass furnace. Careful arrangements have been made in stabilizing the oil supply pressure, atomizing gas pressure and the tightness of the top wire of the sidewall. Through careful preparation and careful operation, after the end of the glass furnace, the inspection of the sidewall blocks found that there were five vertical cracks in the 1# port and left and right, and no transverse cracks were found at the root of the knife handle, and there were no cracks in the fused cast AZS33# knife blocks after the 6# port. Through communication with the glass design institute and other manufacturers in the industry, the company‘s baking glass furnace is very successful in avoiding the explosion of fused cast AZS44# knife handle blocks.
Through the above analysis, it is not difficult to see that the service life of the sidewall blocks directly affects the life of the glass furnace, and when the glass furnace is baked, the explosion of the sidewall blocks is widespread, but as long as we plan carefully and operate carefully, the explosion degree of the sidewall blocks in the process of baking the glass furnace will be reduced to a minimum, and even the explosion of the sidewall blocks can be eliminated, laying a solid foundation for the long life of the glass furnace.
When selecting sidewall blocks for glass furnaces, it is essential to comprehensively consider factors such as the performance of refractory materials, glass furnace operating conditions, and cost-effectiveness.
♦ Fused cast AZS Blocks (AZS Blocks)

Applicable Scenarios: High-erosion areas (e.g., melting tank, sidewalls, throat).
Advantages: Excellent resistance to glass liquid erosion (especially fused cast AZS 33#blocks and fused cast 41# AZS blocks with high ZrO₂ content), high-temperature resistance (above 1700°C).
Note: Avoid contact with alkaline vapors (e.g., in upper structures) to prevent "foaming" phenomena.
♦ α-β Alumina Bricks (Sintered Bricks)
Applicable Scenarios: Medium-to-low erosion areas or glass furnaces requiring high glass quality (e.g., optical glass).
Advantages: Non-polluting, good thermal shock resistance, and lower cost than fused cast AZS blocks.
Disadvantages: Weak erosion resistance, unsuitable for strongly alkaline glass.
♦ Dense Zirconia Bricks (ZrO₂ ≥ 94%)
Applicable Scenarios: Ultra-high erosion environments (e.g., borosilicate glass, electronic glass furnaces).
Advantages: Exceptional erosion resistance, but extremely high cost.
If strong erosion resistance is required, prioritize materials with high ZrO₂ content (e.g., fused cast AZS 41#blocks with 41% ZrO₂).
If the glass furnace undergoes frequent start-ups and shutdowns, pay attention to the material‘s thermal expansion coefficient (e.g., α-β alumina bricks perform better than fused cast AZS blocks).
For more professional advice, please contact us. Henan SNR Refractory Co., Ltd. is dedicated to the manufacture,research and development of fused cast AZS refractory materials and bonded refractory materialsfor glass industry. Meanwhile, SNR can provide total solutions and services for glass furnace design, glass furnace construction, renovation, and upgrading. Please contact me if you have any requirements.
.png) CONTACT: zoe@snrefractory.com/
CONTACT: zoe@snrefractory.com/ WhatsApp:+86 18172389584
WhatsApp:+86 18172389584


