Fused Cast Al2O3-ZrO2-SiO2 Refractory Block (also known as Fused Cast zirconium-corundum, hereinafter referred to as Fused Cast AZS block) is a kind of dense shaped refractory material made by melting the compound containing industrial alumina, zirconia sand and siliconized zirconium and alkali in electric arc furnace, casting it into the sand mold, and then cooling and annealing it in the holding box. This product has high refractoriness, good durability and thermal shock resistance at high temperature, low porosity (≤ 1.5%), strong resistance to erosion of the glass liquid, and are widely used in a variety of glass furnace melting part of the side wall, breast wall, big arch and other parts of the glass furnace, is the key masonry material of the glass furnace. At present, the reasonable allocation of the use of high-quality fused cast refractories materials, float glass furnaces can be used for 10-15 years. End fired furnaces can be used for 9-11 years.
The figure below shows the configuration of fused cast AZS block for float glass furnaces. It can be seen that Fused cast AZS 33#PT and Fused cast AZS 41#ZWS are the most used materials in glass furnaces, accounting for about 80% of the entire glass furnace refractory materials.
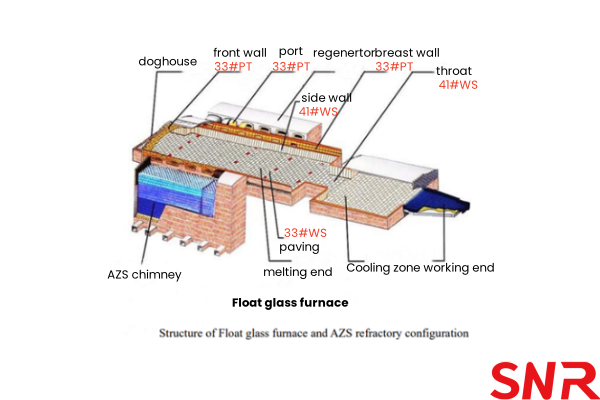
In recent years, the booming development of high-end construction, electronics and photovoltaic industries has promoted the demand for high-quality glass. At the same time, glass furnaces are developing towards large-scale, low energy consumption, zero carbon emissions and long life, which puts higher requirements on the performance of fused cast AZS block. The quality parameters of fused cast AZS block for glass furnaces are important indicators for evaluating their performance and application effects.
The following is an analysis of the quality parameters of this material:
Ⅰ.Chemical composition
Ⅱ. Physical property
Ⅲ. Corrosion protection
Ⅳ. Process
Ⅴ. Quality control
Ⅰ.Chemical composition
The fused cast AZS block is mainly composed of alumina (Al₂O₃), zirconium oxide (ZrO₂) and silicon dioxide (SiO₂). The following is a detailed analysis of these chemical compositions:
1. Alumina(Al₂O₃)
Alumina is one of the components with a higher content in fused cast AZS block, usually around 48%.
It has a high melting point, high hardness, good abrasion resistance and chemical stability, and is an important part of fused cast AZS block.
2. Zirconium oxide (ZrO₂)
The content of zirconia in fused cast AZS block refractories is also quite high, generally between 30% and 45%, depending on the type of material and manufacturing process. Zirconia has excellent high temperature resistance, thermal shock stability and chemical stability, which can significantly improve the overall performance of fused cast AZS block.
3. Silicon dioxide (SiO₂)
Silicon dioxide content in fused cast AZS block refractories is relatively small, generally around 20%.
Together with alumina and zirconia, it forms the matrix of fused cast AZS block and has an influence on the physical and chemical properties of the material.
Each of these three materials is denoted by fused cast AZS blocks. Different models of AZS materials have different chemical composition ratios, such as fused cast AZS 33# blocks, Fused cast AZS 36# blocks and Fused cast AZS 41#blocks.
Fused cast AZS 33# block: Contains relatively low zirconium content and is the basic model in the fused cast AZS block series. It has good resistance to glass liquid erosion and is suitable for general glass furnace environments.
Fused cast AZS 36# block: Compared to AZS33, AZS36 has more zirconia crystals in the form of chain-links and a lower glass phase content. The erosion resistance is further enhanced and it is suitable for use in areas with high glass liquid flow rates or high temperatures, such as critical areas of the side wall near hot spots of the melting end in glass melting furnaces.
Fused cast AZS 41# block: Among the fused cast AZS block series products, fused cast AZS 41# block has the highest zirconium content and contains more evenly distributed zirconium oxide crystals. It has the best erosion resistance among zirconia corundum block systems, with extremely high resistance to glass liquid erosion and very high glass phase exudation temperature, and very low contamination of glass liquid.
The production of Fused cast AZS 33# block requires two main raw materials, industrial alumina (γ-Al2O3) and zircon sand (ZrO2-SiO2), while the production of fused cast AZS 36# block and fused cast AZS 41# block requires the addition of desilicated zirconium (ZrO2) and the replacement of γ-Al2O3 by α-Al2O3. Because zircon sand is a refractory material, in order to decompose it completely into ZrO2 and siliceous amorphous phases at about 1675°C and to melt it completely at about 1900°C, it is necessary to introduce Na2O, K2O or rare earth metal oxides as fluxes, which have the effect of decomposing mullite into corundum and glassy phases, and are able to inhibit mullite precipitation in the alumino-silicate melt effectively. In addition, when the castings are cooled and annealed, the transformation of tetragonal ZrO2 (t-ZrO2) to monoclinic ZrO2 (m-ZrO2) occurs at about 950°C, which is accompanied by a volume change of 6~8%. In order to prevent the martensitic phase transformation of ZrO2 from cracking the casting, a small amount of divalent or trivalent metal oxides, such as CaO, Y2O3, etc., can be added to stabilize part of the t-ZrO2 phase to room temperature and inhibit the extent of the ZrO2 phase transformation, thus improving the manufacturability of the fused cast AZS refractory materials and reducing the cracking. Small amounts of Fe2O3 and TiO2 are present in fused cast AZS refractory materials because zircon ore is usually associated with ilmenite.
The specific chemical compositions are listed below:
|
chemical compositions |
Al₂O₃ |
ZrO₂ |
SiO₂ |
Na₂O |
CaO+MgO+Na2O+K2O |
Fe₂O₃+TiO₂ |
|
AZS-33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The ratio of these chemical components directly affects the physical properties, erosion resistance and service life of the material, and therefore needs to be strictly controlled during the manufacturing process.
1. Density:
The density of fusion cast AZS material is an important indicator of its quality. Usually, the higher the density, the better the material‘s densification, and the stronger the erosion resistance. The density of different types of fused cast AZS materials varies slightly, but is generally between 3.4-3.8 g/cm³, and the density of fused cast AZS 33# WS (Void Free) is usually higher.
2. Linear Expansion:
Linear expansion is a measure of the dimensional change of a material as temperature changes. For refractory materials used in glass furnaces, a lower linear expansion is beneficial. It helps to minimize deformation and cracking at high-temperature.
3. Refractoriness:
fused cast AZS block have high refractoriness, generally up to 1770-2000 ℃, which enables them to work stably at high-temperature for a long time.
4. Thermal conductivity:
Thermal conductivity reflects the material‘s ability to conduct heat. Fused cast AZS block have a low thermal conductivity, which helps to minimize heat loss and improve the thermal efficiency of the glass furnace. 
|
Performance indicators |
AZS-33 |
AZS-36 |
AZS-41 |
|
Density(g/cm³) |
3.35-3.75(depending on casting method) |
|
|
|
Stomatal percentage(MPa) |
|
|
|
|
Compressive strength(℃) |
|
|
|
|
Glass Phase Exudation Temperature(%) |
|
|
|
|
Bubble precipitation rate |
|
|
|
|
Speed of resistance to glass erosion |
|
|
|
Below are product descriptions for all three products:


(1)Appearance and casting properties
The surface layer is brightly colored, and the interior shows white or beige color caused by oxidation. There are no internal air holes, and it has good castability and can be molded into various shapes. --The regular casting (PT) varieties have excellent castability and can be made into blocks of various shapes and sizes, such as breast wall blocks, feeder entrance blocks, peel hole blocks and so on. –Void free casting (WS) varieties, through the special casting means and or processing means, can be used for special parts of a variety of specifications of straight blocks and a variety of shapes of shaped blocks.
(2) Performance in glass furnaces
1550 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, erosion resistance index of 100;
1100 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, the tendency to precipitate bubbles index of 1 ~ 2;
1500 ℃, the surface precipitation crystal phenomenon is basically no;
1450 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, the tendency to stone index of 1 ~ 2.
(3) Recommended slurries
A. AZS33 powder is used for the base layer of the glass furnace paving and the embedding of electro fused blocks.
B. Zirconium mud (ZrO2>60%, Al2O3≤0.4%, Fe2O3≤0.1) should be used for transition in contact with siliceous refractories.
Masonry: regular casting or tilting casting blocks in the masonry must make its casting hole surface facing out. The surface with casting holes should not be used as the contact surface.


(1) Appearance and casting properties
Bright color on the surface, white or beige inside due to oxidation, no connecting pores inside. A variety of straight blocks and simple shaped blocks can be produced, and large-sized blocks can be produced by end casting process.
(2) Performance in glass furnaces
1550 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, erosion resistance index of 110;
1100 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, precipitation bubble tendency index of 1 ~ 2; 1500 ℃, the surface precipitation crystal phenomenon is basically no;
1450 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, stone tendency index of 0 ~ 1.
(3) Recommended slurries
A. AZS33 powder should be used for the base of the glass furnace paving.
B. In contact with siliceous refractories, zirconium mud (ZrO2>60%, Al2O3≤0.4%, Fe2O3≤0.1) should be used for transition.
C. The residual shrinkage of the end casting side wall blocks are very small, and the tail end is facing down when it is used, and the residual shrinkage should be filled with AZS33 powder before block laying.


(1) Appearance and casting properties
Bright surface color, white or beige inside due to oxidation, no connected air holes inside. It can be cast into rectangular bodies of various sizes, and simple shaped blocks can be produced by the end casting process, and large-sized blocks can be produced by the end casting and void free casting process.
(2) Performance in glass furnaces
1550 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, anti-glass liquid erosion index is 130; 1100 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid, precipitation bubble tendency index is 1 ~ 2; 1500 ℃, the surface precipitation crystal phenomenon is basically no;
1450 ℃ contact soda-lime glass liquid stone tendency index is 0 ~ 1.
(3) Recommended slurries
A. AZS33 powder should be used for the base of the glass furnace paving.
B. In contact with siliceous refractories, zirconium mud (ZrO2>60%, Al2O3≤0.4%, Fe2O3≤0.1) should be used for transition.
C. The residual shrinkage of the end casting side wall blocks are very small, and the tail end is facing down when it is used, and the residual shrinkage should be filled with AZS33 powder before block laying.
The erosion of fused cast AZS refractory blocks by liquid glass is a complex physical and chemical process. For the fused cast AZS block itself, the erosion rate depends on the chemical composition and microstructure of the material. It has been demonstrated that the high erosion resistance of fused cast AZS block is due to the well-developed plagioclase zircon and corundum crystalline phases.
In the chemical composition of fused cast AZS blocks, ZrO2 is the most erosion-resistant component, and the higher its content, the denser the structure of the refractory material; Al2O3 is a neutral substance, which easily reacts with the alkaline components in the glass solution, and thus has a weaker erosion-resistant property; SiO2 has a two-fold nature: too high a content of SiO2 will increase the glassy phase, leading to a certain degree of exudation of glassy phases from the fused cast AZS material, which is a major factor in the erosion-resistant nature of the material.
Fused cast AZS block bubble precipitation rate has a negative impact; SiO2 is too little, the glass phase is too small, the viscoelasticity of the refractory material is reduced, is not conducive to buffer the phase change stress during cooling, AZS castings are prone to cracking. In the erosion process, the glass liquid will penetrate along the cracks to make the material damage.
Therefore, the chemical composition and structure of the material can be optimized by regulating the ratios of SiO2/Na2O and ZrO2/SiO2 in the production of fused cast AZS blocks in general. At SiO2 : Na2O = 12 and ZrO2 : SiO2 = 2, fused cast AZS materials are generally more resistant to glass erosion.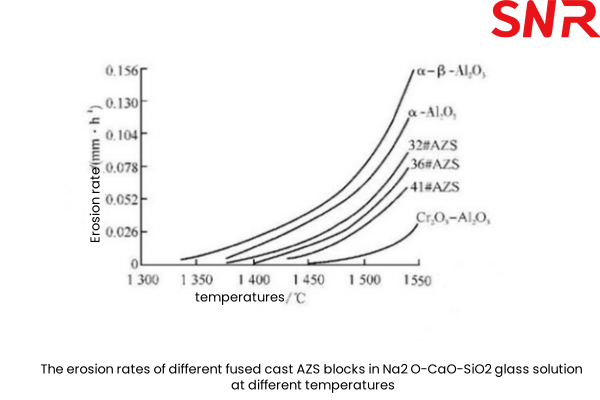
The following figure shows the erosion rates of different fused cast AZS blocks in Na2 O-CaO-SiO2 glass solution at different temperatures after 95 h test. From Fig. 1, it can be seen that: below 1400 ℃, the erosion rate of each fused casting material is very small; above 1400 ℃, the erosion resistance is in the following order: Cr2O3 -Al2O3、41# AZS、36# AZS、33# AZS、α-Al2O3、α-β-Al2 O3
Usually fused cast AZS 41# is used for harsh parts, fused cast AZS 36# is used for medium erosion parts, fused cast AZS 33# is used for relatively mild parts; β-Al2O3 blocks can be used in the breast wall of the cooling section, and α-β-Al2O3 fused blocks can be used in the side wall and paving blocks of the cooling section. In recent years, refractory manufacturers around the world to significantly increase the cast zirconium corundum material ZrO2 content, such as 33 # AZS ZrO2 content increased to 34% ~ 35% (w); 36 # AZS ZrO2 content increased to 37% ~ 39% (w); 41 # AZS ZrO2 content increased to 43% ~ 45% (w), the resistance to corrosion is also greatly enhanced.
The erosion resistance of fused cast AZS block is related to the overall life time of glass furnaces. In practice, fused cast AZS refractory blocks are the refractory of choice for direct contact with the glass furnace due to their high densification, low total porosity, richness in chemically stable ZrO2 and Al2O3 components, and the complete development of corundum and ZrO2 crystals with a high degree of bonding between the crystals and the filling of the crystal skeleton with glass phases.
The production process of fused cast AZS blocks is divided into seven stages: technical study, composition, fusion, shaping, annealing, finishing and pre-assembly.
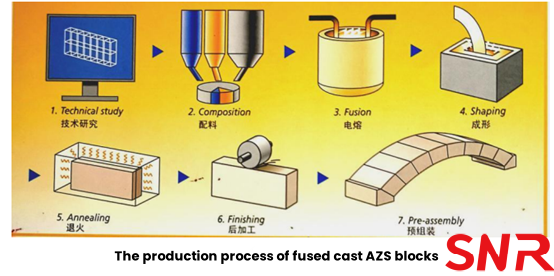
(1) Technical study
►Check carefully the technical standards and requirements of the delivered products in the purchase contract
►According to the information provided by the customer, study and judge whether the customer‘s requirements are reasonable in the application of glass furnace, and put forward the preview or improvement suggestions to the unreasonable places, so that the customer will be the high-quality Fused cast AZS Block and the whole glass furnace to get the best matching use.
Sand manufacturing
►The sand molds used in the production of fusion casting AZS refractory materials are mainly water glass sand mold and resin sand mold. The water glass sand type uses water glass as the bonding agent, and the sand plate is made and dried, and then assembled into the required sand type. Resin sand is mixed with curing agent and silica sand according to the proportion, and then filled with sand according to the required sand type at one time and molded naturally. The production efficiency and precision of resin sand mold is higher than that of water glass sand mold. In addition, the resin sand mold will naturally collapse after casting, eliminating the cleaning process of water-glass sand molds and resulting in a shorter manufacturing cycle.
(2) Composition
►Matching materials formulated with high-quality raw materials
►In a clean and tidy environment, using a high-precision electronic weighing system, raw materials such as industrial alumina powder, zirconium sand, desilicated zirconium, and soda ash are accepted and qualified, and then sent to the raw material workshop for pre-treatment, and then proportioned and uniformly mixed according to the requirements of different products.
(3) Melting/fusion
►Add the materials into the three-phase electric arc furnace for melting, and blow the oxygen with the oxygen gun synchronously. The key to the melting process is to maintain a stable melting temperature, minimize the carbon content in the material, so that the low-value impurities in the high-value state, to get a uniform chemical composition, with a certain temperature and good casting performance of the melt. Melting temperature should be moderate, low temperature can not make highly uniform melt, easy to make the castings form holes; temperature is too high easy to make the castings produce serious segregation.
(4) Pouring/shaping
►The melted composite is poured into a specially designed sand mold. The key to the casting process is that the melt should be properly superheated, so that the fused cast AZS blocks will have concentrated shrinkage holes and thick dense zones. However, when the degree of superheat is too high, easy to make products form cracks and large shrinkage holes. Commonly used there are four main casting methods:
---Regular casting (PT for short) adopts ordinary riser casting, with large shrinkage holes, which can extend to 30%~50% of the height of the block body, and is used for casting fused cast AZS blocks used in low-temperature glass-contact or non-glass-contact zones.
---Tilt casting (QX for short) is a sand mold tilt placed at a certain angle, the riser is located in the upper end of the sand mold, so that the shrinkage holes are concentrated at one end, most of the products are denser, used for casting rectangular shaped blocks for the side wall.
---Void free casting (WS for short) is set up in the casting of large-sized risers, shrinkage holes concentrated in the risers, cut out when finishing, the remaining part of the casting composition is uniform, dense organization, used for casting in the glass furnace scouring the most serious areas (liquid flow holes) or there are a number of exposed surface areas (doghouse, side walls paving, etc.).
---End casting (ZWS for short) is made from the end of the block opposite to the metal line and the major shrinkage cavity is cut off. This structure effectively resists the erosion of the liquid glass and reduces the formation of stones or other defects in the glass furnace, and is used in a number of parts of the glass furnace, including the superstructure of the melting end, the side walls and paving of the working end, and the forehearth. Its good erosion resistance and mechanical strength make it useful in these critical areas.
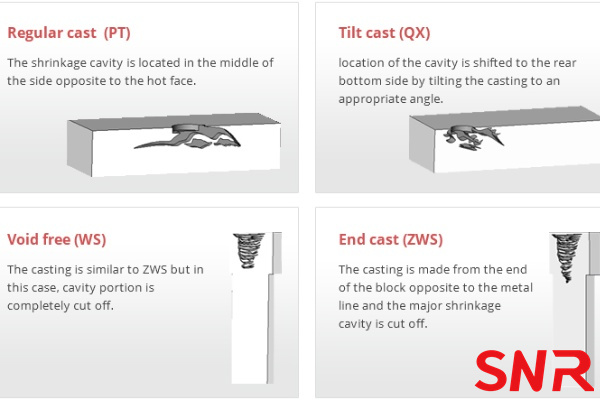
At present, in order to make the service life of the glass furnace longer, most of the side wall blocks use the WS casting method.
(5) Annealing
►Slowly cool the fused cast AZS blocks for 7 to 14 days, controlling the cooling rate all the way down to the room temperature level to avoid cracks in the block body.
►Usually use the heat preservation box filled with diatomaceous earth, alumina hollow ball and other thermal insulation materials with mold annealing, can also be used in tunnel furnace at a certain temperature regime with mold or demolding annealing.
►The return area should be as airtight as possible
(6) finishing
►After annealing, the fused cast AZS blocks are cleaned to remove all impurities brought in by the sand mold. Initial inspection of the blocks is carried out to exclude defective blocks. After further inspection, the blocks are blasted, cut and pre-assembled according to the surface finish, size and seam tolerances provided by the customer. Each Fused cast AZS block must be cleaned with a diamond abrasive, blasted and sanded on each block to give the block a smooth surface.


(7)Pre-assembly
►Assemble the blocks on the platform to form a certain part of the glass furnace, check the overall size of the assembled part and whether the quality of the joints meets the customer‘s requirements.
The manufacturing process of fused cast AZS blocks also has an important impact on their quality. Although these three types of fust cast AZS blocks in the manufacturing process may be similar, but due to the different zirconium content, the specific melting, refining, casting and other process parameters may be adjusted, so in the manufacturing process need to strictly control the ratio of raw materials, melting temperature, casting speed and annealing process and other parameters, in order to ensure that the material‘s composition is uniform, structural densities and stable performance.
In terms of quality control of fused cast AZS blocks for glass furnaces, the main focus is on the following aspects:
1. Raw material selection

The chemical composition of fused cast AZS refractories is one of the key factors in determining its crystalline structure and physical and chemical performance indicators, therefore, effective control of the chemical composition of the product to stabilize and improve the quality of fused cast AZS block products is very important. From the source to choose high purity raw materials. Especially Al ₂ O ₃, ZrO ₂ SiO ₂, Na ₂ O and other major components of high precision purity, reduce harmful impurities. Only in this way can the product crystalline structure optimization, physical and chemical performance indicators to meet the glass melting furnace at high-temperature anti-erosion, anti-washout function
2. Use advanced product preparation technology and equipment
Fused cast AZS refractory blocks of crystalline phase composition is fused cast AZS block products excellent physical and chemical properties of the concentration of its crystalline phase composition for the plagioclase zirconia, corundum and its two co-crystals, through which the generation of the glass phase tightly arranged bead-like combination of different products with different composition of the crystalline phase, the physical and chemical properties are also different, this generating process is a high-temperature melting through the arc furnace, so that the melt to achieve excellent homogenization of the ingredients and Casting and annealing process of strict temperature control and the formation of. 
At present, most of the production enterprises are using oxidation melting production, this melting process to solve the problem of high carbon content in the reduction method used in the past, high carbon content will increase the product porosity, reduce the bulk density and the glass phase precipitation temperature, but also reduces the product resistance to erosion, and at the same time, in the use of glass melting furnace to increase the air bubbles in the glass, reducing the quality of the glass. The oxidation production technology now used overcomes the disadvantages of inconsistent product quality caused by outdated processes in reduction production, improves the quality of the fused product, and accordingly ensures the service life of the glass furnace.
In addition, in the whole process of preparation of fused AZS refractory blocks, there should be strict scientific operation procedures and standards for mold making, raw material preparation, melting in electric arc furnace, casting and annealing, etc., and the quality of the products can be greatly affected by the problems in each process and link. For example, in the oxygen blowing process of the high-temperature melting of the compound in the electric arc furnace, it is necessary to operate strictly according to the process parameters, such as the angle of oxygen blowing, the time of oxygen blowing, the pressure, the flow rate and the depth of insertion of the oxygen gun.
3.Production process monitoring
Each process should continue to design and use advanced self-control detection means, such as the choice of isotope low-energy emission spectrometer and electronic weighing and dosage system combined with a short time reaction to the raw materials with the material, molten material detection data, temperature digital controller, melting process TV monitor, high-efficiency with the material mixing equipment, mold integrative production equipment, mechanized pouring equipment, control of annealing devices, and so on, a series of high-tech Means of detection and equipment, all have an important role in stabilizing and improving the quality of casting products. Large-scale selection of modern high-tech monitoring and testing means and equipment is casting refractory products to standardization, integration and modernization of the necessary way.
4. Finished product inspection
Glass furnace/kiln according to the accuracy of the design requirements of the structure size, in addition to the quality of masonry construction reasons, the exact dimensions of the molten product is also very relevant. If the product dimensions cannot be guaranteed, the glass furnace structure size cannot be guaranteed, in the glass furnace masonry process is prone to skewed, block gap is too large, the block body plane bite is not flat, surface roughness, assembly of the block body mismatch and other defects, which will result in glass furnace baking furnace and normal operation of accidents or serious erosion, as well as contamination of the glass of the serious consequences of the impact of the service life of the glass furnace.
For this reason, the casting products must be cold processed, the introduction of new high-efficiency and high-precision cutting machine, plane, inclined and curved surface grinding machine tools and drilling and other ancillary processing equipment, so as to meet the structural dimensions of the glass furnace on the refractory material size accuracy requirements to realize the casting of products assembled with precision matching, according to the requirements of the design drawings provided to the user.
Strict chemical composition analysis, physical property test and erosion resistance test are carried out on the finished products, including appearance quality, dimensional accuracy, physical properties (such as compressive strength, refractoriness, etc.) and chemical properties (such as erosion resistance, etc.) of the test.
In summary, the quality parameters of fused cast AZS refractories for glass furnaces include chemical composition, physical properties, erosion resistance and other aspects. By strictly controlling these parameters and continuously optimizing the manufacturing process and quality control procedures, Fused cast AZS refractories with excellent performance and long service life can be produced to meet the needs of the glass manufacturing industry.
Henan SNR Refractory Co., Ltd (SNR) is professional in producing high-quality Fused Cast AZS Blocks for glass furnaces. If you have any needs, please contact me!
Email:zoe@snrefractory.com
Web:www.snr-azs.com 




