For fused cast AZS blocks, the phenomenon of expansion is very common. However, this expansion will have some impact on its use, so it is necessary to understand the cause of this phenomenon.
Let‘s take a look at the reasons for the expansion of fused cast AZS blocks:
1.Raw materials
2. Firing temperature and porosity
3. Usage environment
4. Physicochemical reaction
5. Thermal expansion properties
6. The methods to prevent the expansion of fused cast AZS blocks can be started from various aspects.
The raw materials of fused cast AZS block mainly include zircon sand, industrial alumina powder and small amounts of Na2O and B2O3 fluxes. If the raw materials contain clay minerals or their decomposition products, these substances are easy to absorb water and undergo swelling reaction in humid environment, which will affect the stability and swelling reaction of the block at high temperature.


2. Firing temperature and porosity
The firing temperature of fused cast AZS block has an important influence on its structure and properties. During the high temperature firing process, the materials in the raw materials will undergo a series of physical and chemical reactions to form a stable crystal structure and glass phase. If the firing temperature is not controlled properly, it may cause too many pores or cracks inside the block, which may affect its expansion performance.
Porosity is an important indicator to measure the compactness of refractory materials. If the porosity of fused cast AZS blocks is too high, it means that there are more pores and cracks inside the material. These pores and cracks are easily eroded and penetrated by water, gas and other media during use, resulting in increased expansion.
►Humid environment
When used in a humid environment, fused cast AZS blocks are continuously heated and cooled. This thermal stress cycle causes stress concentrations and the expansion of microcracks inside the block, which in turn exacerbates the expansion phenomenon. In addition, water molecules easily penetrate into the material, spreading along the microcrack walls and causing cracks to expand.
The diameter of water molecules is about 0.2 um, while the particles that form the fused cast AZS block material are about 1000 times or even larger than the water molecules. Due to the thermal movement of fused cast AZS blocks, water molecules can easily penetrate into the material, causing the formation of fine cracks. When the vapor or water molecules diffuse along the micro-crack wall reach a narrow position, the pressure acting on the crack sidewall increases to more than 100 MPa, resulting in the expansion of the crack.
►High temperature environment
In the high temperature environment such as glass industry glass furnace, fused cast AZS block is subjected to the action of high temperature glass liquid for a long time. The alkaline components (such as Na2O) in the glass liquid will invade the block along the pores and cracks of the block body, diffuse and penetrate with the precipitated glass phase, resulting in the loosening and expansion of the block body structure.

►Adsorption and diffusion of water vapor
Water vapor absorbs on the capillary walls of fused cast AZS blocks and may form hydrates or melts. The formation of these compounds will increase the volume of the block, resulting in expansion.
►Hydration of glass phase
Fused cast AZS block contains a certain proportion of glass phase. In high temperature and humid environment, the glass phase is prone to hydration reaction, resulting in the formation of a larger volume of hydrate, resulting in block body expansion.
►The influence of clay minerals and their decomposition products
If the raw material contains clay minerals or their decomposition products, these substances are prone to absorb moisture and undergo a swelling reaction in a humid environment, which in turn affects the swelling performance of the entire fused cast AZS block body.

5. Thermal expansion properties
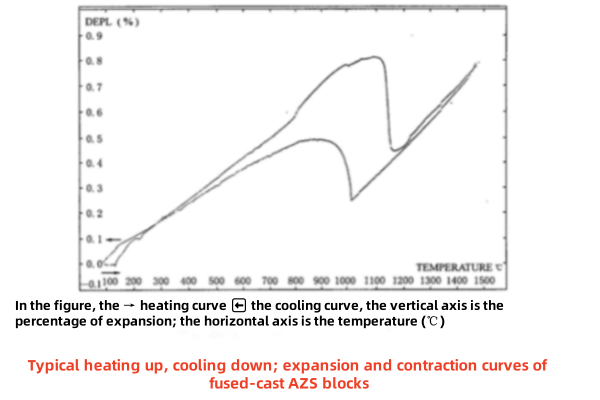
The thermal expansion properties of fused cast AZS blocks, of which the three compositions 33, 36, and 41 are essentially the same. Their thermal expansion, contraction temperature are exactly the same, only the maximum expansion and contraction amount has some differences.
Temperature expansion, contraction curve in some special circumstances for the glass furnace cooling measures to provide a basis.
►Expansion at elevated temperatures and characterization of the contraction curve:
0~800℃,expansion rate:0.55%
800~1100℃,expansion rate:0.27%,(At 1100 ° C, the maximum expansion rate is 0.82%.)
1100~1160℃,contraction rate0.37%,(At 1160 ° C, the remaining expansion rate is 0.45%.)
1160~1550℃,expansion rate:0.37%,(At 1500 ° C, it rises to a maximum expansion rate of 0.82%.)
During the period from 0 to 800 ° C, the expansion rate of fused cast AZS blocks is 0.55%. During this period, about 500 ° C is the expansion period of silicon bricks, so this period can be divided into two stages of heating rate.
Before 500 ° C: preferably 5 ° C/h, mainly considering two points, one is the expansion period of the silica brick; the other is to remove moisture from the glass furnace.
During the period of 500 to 800 ° C, the heating rate can be appropriately increased to 10 ° C/h, but the maximum cannot exceed 15 ° C/h. This is because the heating rate is too fast, which will generate great tensile stress and prone to cracking.
During the period of 800~ 1100 ° C, the expansion rate of fused cast AZS blocks is the highest. The cumulative expansion rate has reached 0.82%, and the heating rate is preferably 10 ° C/h. During this heating stage, the expansion joint and the part with considerable length cannot be reserved in the glass furnace. (For example, the "C" block in the float glass furnace; the weir block in the end fired glass furnace, etc.).
To properly relax the pull strip or top wire, the relaxation degree can refer to the following calculation methods:
Operating temperature: around 1300 ° C, the degree of relaxation = the length of the expansion site * 0.45% - the brick crack can absorb the maximum amount of expansion.
Operating temperature: around 1500 ° C, the degree of relaxation = the length of the expansion site * (0.45% + 0.37%/2) - the brick crack can absorb the maximum amount of expansion.
Determination of the maximum amount of absorbable expansion in the brick crack: empirically derived based on the accuracy of the brickwork and the state of the masonry.
When the glass melting furnace starts to run normally, lock all the drawbars and top wires tightly.
During the period of 1100~ 1160 ℃, the fused cast AZS block began to shrink due to the transformation of zirconia crystal form, but soon began to expand again. At this heating stage, the heating rate of the glass furnace can be controlled at 10 ℃/h, and attention should be paid to observe the condition of the fused cast AZS block inside and outside.
After 1160 ° C to the normal operating temperature, the heating rate of the glass furnace can also be controlled at around 10 ° C, and the expansion requirements of the silicon bricks should also be taken into account.
►Cooling Shrinkage, Expansion Curve Characteristics
1500~1020°C, shrinkage rate 0.57% (0.82% to 0.25%);
1020~900°C, expansion rate 0.22% (0.25% to 0.47%);
900~0°C, shrinkage rate 0.47% (0.47% to 0)
The cooling shrinkage and expansion curves provide the basis for glass furnaces to take measures under special circumstances. Some glass furnaces will cool down to repair the glass furnace, cool down to stop the glass furnace, and then ignite. Or continue to use used fused cast AZS blocks after stopping the glass furnace. These situations often occur in actual work. Therefore, it is necessary for us to grasp the characteristics of cooling shrinkage and expansion of fused cast AZS blocks. The basic principle is that the cooling speed can be appropriately released faster than the heating speed of the glass furnace. The cooling speed can be 20-30 ° C/h, but the most important thing is that the cooling speed should be uniform, and cold air should not be blown into the inside of the glass furnace. The outer insulation block of fused cast AZS blocks is best removed when the internal temperature of the glass furnace drops below 800 ° C.

It is worth noting that in the traditional glass furnace process, the heating rate before 500 ° C is still more appropriate. However, after 800 ° C, especially after a fire, the heating rate is not controlled or poorly controlled, and some fused cast AZS blocks will have horizontal cracks and vertical cracks, which will affect the use effect.
Therefore, we provide some discussion suggestions:
① In-depth understanding of the formation of thermal stress and its thermal properties of fused cast AZS blocks.
② Heating rate: before 500 ° C, 5 ° C/h. After 500 ° C, about 10 ° C/h, (but not more than 10 ° C/h). Also consider the expansion requirements of silicon bricks.
③ Appropriately increase the temperature of the "fire", preferably at 1100 ° C, to avoid the heating rate being difficult to control.
Of course, there were reliable means to control the heating rate, which could reduce the temperature of the "fire". For a furnace fueled by gas, it was better to increase the temperature of the "fire".
④ Reserved amount of expansion joint
When the operating temperature is about 1300 ° C, the reserved amount of the expansion joint = the length of the expansion part * 0.45%
When the operating temperature is around 1500 ° C, the reserved amount of the expansion joint = the length of the expansion part * (0.45% + 0.37%/2)
⑤ Treatment method of not allowing reserved expansion joints: Take the measure of "loosening first, then tightening". For the specific "degree of relaxation", please refer to the relevant calculation method in 5.1 above.
⑥ The temperature in the fast-heating glass furnace should be uniform. It is impossible to make the temperature uniform without hot air, and it is not feasible to use a burner to quickly bake the glass furnace, and the result will be very dangerous.
⑦ During the heating up of the glass furnace, when the temperature drops occasionally, it is recommended to use rapid reheating, preferably within 2 hours, to match the original heating schedule.
⑧ The sidewalls tiles are cooled, and the blast opening temperature is recommended to be below 500 ° C to avoid large thermal stress caused by high temperature cooling and blowing.
⑨ It is recommended that the cooling of the sidewall blocks should be arranged according to the temperature of the cooling air flow and air pressure, and can be adjusted.
The purpose is to control the size of the thermal stress generated by the sidewall blocks and avoid or reduce the cracks of the block body. The cooling air is set in different regions, and the flow and air pressure can be adjusted, which is very important for the maintenance of the glass furnace during the heating glass furnace, during operation, and in the later stage of the melting glass furnace.
⑩ Determination of the height of the non-thermal insulation area of the sidewall block: the larger the height, the smaller the thermal stress generated by the brick body. The smaller the height, the greater the stress. Considering the heat dissipation conditions of the liquid surface line, the size of the thermal stress generated by the block body, sidewall insulation effect. We SNR think the height of about 300mm is more appropriate.


6. The methods to prevent the expansion of fused cast AZS blocks can be started from various aspects.
Here are some of the main methods:
►Optimize the selection and ratio of raw materials
Selected raw materials
Select raw materials with stable chemical composition and low impurity content to ensure that the quality of raw materials meets production requirements.
Reasonable ratio
According to the use environment and performance requirements of the product, adjust the ratio of raw materials reasonably to reduce the content of ingredients with a high tendency to swell.
►Strictly control the firing process
Optimize the sintering temperature system
Formulate a scientific and reasonable sintering temperature curve to ensure that the block body can be fully sintered at high temperature, forming a dense crystal structure and glass phase, and reducing the generation of pores and cracks.
Control the heating rate and holding time
The appropriate heating rate and holding time help the materials in the raw material to fully react and diffuse, reducing the formation of internal stresses and defects.
►Improve the use environment
Keep dry
Keep dry in an environment where fused cast AZS blocks are used to reduce the penetration of water molecules and other media and reduce the risk of swelling.
Regular maintenance
Conduct regular inspections and maintenance of fused cast AZS blocks in use to detect and deal with hidden dangers that may lead to expansion in a timely manner.
►Adoption of special treatment techniques
Surface coating
Apply a layer of waterproof, anti-corrosion and other functions to the surface of fused cast AZS blocks to isolate the penetration of water molecules and other media.
Heat treatment
Heat treatment of fused cast AZS blocks, such as annealing treatment, is performed to eliminate internal stresses and defects and improve the stability and anti-expansion properties of the block body.
►Other matters needing attention
Reasonable design
When designing and using fused cast AZS blocks, their expansion performance should be fully considered. Allow sufficient expansion space or take other measures to prevent damage to equipment or structures from expansion.
Quality control
Strengthen the quality control and testing in the production process to ensure that the performance indicators of fused cast AZS blocks meet the standard requirements.


Henan SNR Refractory Co., Ltd (SNR) is professional in producing high-quality Fused Cast AZS Blocks for glass furnaces. If you have any needs, please contact me!
Email:zoe@snrefractory.com
Web:www.snr-azs.com 


