Fused cast AZS blocks are the key refractory materials for glass furnaces. If fused cast AZS blocks have defects, it will not only shorten the life of the glass furnace, but also cause the surrounding blocks to fall, pollute the glass liquid, and affect the product quality.
In addition, defects such as cracks or pores in fused cast AZS blocks will become channels for heat dissipation. When the glass furnace is operating normally, heat will leak to the outside through these defects, which not only wastes energy but also increases production costs. Therefore, in this article, I will analyze the causes of defects in fused cast AZS blocks and propose solutions.
1. Defects in the casting and annealing of fused cast AZS blocks
2. Analysis of the causes of cracks in fused cast AZS blocks
1. Defects in the casting and annealing of fused cast AZS blocks
1.1 Physicochemical inhomogeneity
The fused cast AZS blocks will produce various defects in the production, which will lead to the poor quality of the products. The physical and chemical inhomogeneity of fused cast AZS blocks is often the main reason for the defects of fused cast AZS blocks. The particles in the mix that are not melted and the gases and inclusions that have not been discharged from the melt in time are physical inhomogeneities. The difference in melt composition along the depth of the glass furnace belongs to chemical inhomogeneity.
1.2 Defect morphology
The defect patterns and their causes in the production of fused cast AZS blocks are listed in the table below.
|
|
Causes of defects in the production process |
|
|
Compound preparation |
Blending |
|
|
|
|
The melting thermal system in the furnace is destroyed, the melting temperature is low, and the melting cycle is insufficient (insufficient unit power consumption). |
|
|
|
After the furnace body is eroded, water invades the space in the furnace; the melting temperature is low; during melting, debris from graphite electrodes and duct joints falls into the furnace for a long time. Infiltration of oxygen, air and other gases. |
|
|
|
Melting time is long, individual components evaporate; heavier components are deposited at the bottom of the furnace; the thermal system is damaged during melting (working under the arc system for a long time) |
1.3 The reason of the defect
In fact, the common reason of defects is due to the breakdown of the temperature regime.
When the fused cast AZS blocks hardens in a closed container (if there is no subsequent melt to replenish it), shrinkage will occur due to shrinkage, which is the main defect of fused cast AZS blocks.
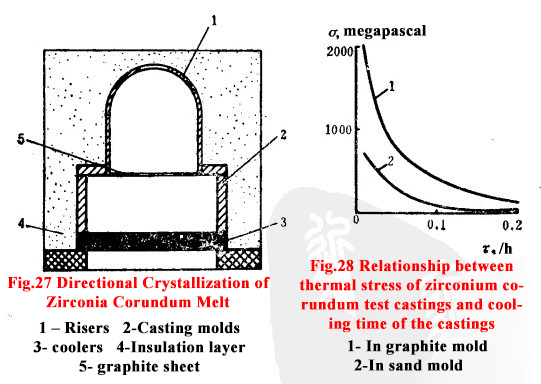
The main way to overcome shrinkage in the production of fused cast AZS blocks is to add a riser to the upper part of the casting mold to supplement the casting of the fused cast AZS block, and at the same time cool the bottom of the mold to allow the melt to crystallize from bottom to top. In order to ensure the formation of such crystallization, it is necessary to maintain a high temperature on the upper horizontal surface of the fused cast AZS block and keep the bottom temperature of the casting mold low. With the help of bottom-up heat evolution, uniform directional crystallization is possible to obtain a dense fused cast AZS block with a small porosity.
However, to remove shrinkage cavities in fused cast AZS blocks, the riser should meet the following conditions:
♦ There should be sufficient melt in the riser at a higher temperature than that of the fused cast AZS blocks.
♦ Choose the riser and the part where the riser is installed correctly.


The above conditions are based on extensive experience in metal casting and the production of the Fused cast AZS 33 #block, and the riser in each specific case must be calculated. There are many basic methods for calculating the riser, some of which are proposed under purely experimental conditions, and some are derived theoretically. The difficulty of using a large riser is that it is very difficult to remove it from the solidified fused cast AZS block, and it requires a considerable number of diamond cutting tools to cut it.
According to the experience of metal casting, an easy-to-remove riser was used in the production of fused cast AZS blocks. That is, between the riser and the fused cast AZS block, a graphite sheet with a hole is installed (as shown below). This sheet has "small flanks", which are easily broken or easily cut off after the melt solidifies. The purpose of making a sheet of such thickness with such a material is to avoid difficulties when supplementary casting of the paving: pieces through the riser. In addition to shrinkage, cracking is also defects formed by the fused cast AZS blocks during melt casting and cooling.
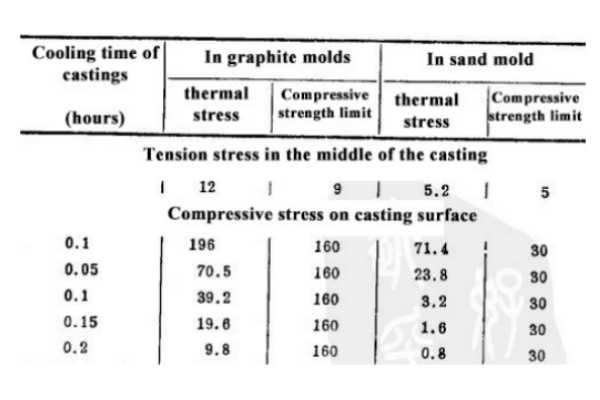
The research on the cracking properties of fused cast AZS blocks shows that there is an obvious relationship between the increase of temperature drop and cooling rate on the section of fused cast AZS blocks and cracking. Therefore, it can be determined that the temperature drop from safety to cracking is 230 ° C, and when the temperature drops to 180 ° C, the product can be guaranteed not to crack. The calculation of temperature field and thermal stress of the test fused cast AZS blocks, the calculation of heat exchange between the fused cast AZS block and the casting mold and the diatomaceous earth insulation material under different conditions, all prove that: The compressive stress generated on the surface of the fused cast AZS block is about 60 - 200 trillion Pascal (Fig. 28), which under any conditions has exceeded the strength index of the fused cast AZS block, and the strength index of the fused cast AZS block is 30 - 160 trillion Pascal (Fig. 29). The tensile stress generated in the center of the fused cast AZS block, depending on the cooling conditions, is 5.2-12 trillion Pascals, which exceeds the strength index of the fused cast AZS block cast in the graphite mold, but does not exceed the ultimate strength value of the cast AZS block when cooled in the sand mold. Therefore, microcracks (cracks) that are not too deep on the surface of the fused cast AZS block will appear in any case, and deep cracks inside the melt cast in the graphite mold are very likely.

1.4 Workaround
Using controlled annealing temperature system in tunnel annealing furnace can eliminate the cracks in fused cast AZS block.
Another reason for the formation of cracks in fused cast AZS block is the porosity and inhomogeneity of the structure, with a certain volume of unmelted "cold" melt. When it cools poorly, the formed AZS block will be porous, and the strength of the AZS block will be reduced by 1/2-2/3.
Therefore, even the thermal stress that is safe for dense fused cast AZS block can damage porous AZS blocks. This phenomenon can often be seen in industrial AZS blocks, where cracks in AZS blocks extend from the center to the surface of the AZS blocks. It can be seen that fused cast AZS blocks at high temperatures will produce cracks when they begin to cool, which can be seen on the surface of clean AZS blocks (carbon is oxidized).

2. Analysis of the causes of cracks in fused cast AZS block
2.1 Production process related reasons
►Improper temperature control
During the cooling process after casting, if the cooling rate is too fast, the temperature layer inside and outside the fused cast AZS block will increase rapidly, resulting in greater thermal stress. When the thermal stress exceeds the strength limit of the material itself, cracks will be caused. For example, during the crystallization process, too fast cooling may make the block body too late to release the internal stress, resulting in cracks.
In some specific temperature ranges during the production process, fused cast AZS blocks may undergo physicochemical changes such as crystal transformation, accompanied by volume changes. If the temperature control is unstable at this time, cracks will be caused by the stress generated by the volume change. For example, at around 1008 ° C, clinoclinic zircon will transform from a high-temperature cubic crystal system to a monoclinic crystal system, accompanied by large volume expansion. If the temperature control is not good, cracks are prone to occur.
►The proportion of ingredients is unreasonable
The composition and ratio of raw materials have an important impact on the performance of fused cast AZS blocks. If the content of some ingredients in the ingredients is too high or too low, it may affect the structure and performance of the block body, making it more prone to cracks. For example, when the silicon content is high, a certain amount of mullite may be produced, which affects the qualification rate and performance of the product and increases the possibility of cracks.
►Molding process problem
During the molding process, if the block body is pressed unevenly, the pressure is insufficient, or the mold design is unreasonable, etc., it will lead to uneven internal structure of the block body, which is prone to stress concentration during subsequent use or treatment, and then lead to cracks.

2.2 Reasons related to the use process
►Thermal Shock
When used in high-temperature equipment such as glass furnaces, fused cast AZS blocks are subjected to frequent and drastic changes in temperature, i.e. thermal shock. For example, when the temperature fluctuates greatly during the opening and closing of the glass furnace or during the production process, the thermal stresses generated by the different rates of temperature change on the surface and inside the block body may lead to cracks. The damaging effect of thermal shock on the block body is especially pronounced when the block body has already been subjected to a certain degree of wear or erosion.
►Mechanical stresses
Mechanical stresses on fused cast AZS blocks are caused by the movement of materials in the glass furnace, scouring of air currents, and vibration of equipment. If the strength of the block body is not strong enough to resist these mechanical stresses, cracks will appear. For example, during the operation of the glass furnace, the flow of materials may cause friction and impact on the surface of the block body, which will lead to cracks in the block body under long-term action.
►Chemical Erosion
Chemical erosion of fused cast AZS blocks may occur due to the presence of glass liquid in the glass furnace. When the block body is subjected to chemical erosion, its structure and performance will change, the strength will be reduced, and cracks are more likely to occur. Moreover, the reaction products from chemical attack may form stresses within the block body, accelerating the cracking process.
2.3 Other factors
►The thermal insulation effect of the incubator is not good.
Insufficient insulation capacity of the incubator will cause the temperature of the fused cast AZS block to drop too quickly during the cooling process after casting, increasing the risk of cracks. For example, improper selection of insulation materials, unreasonable structural design of the incubator, etc., may affect the insulation effect.
►Damage during transportation and installation
When transporting and installing fused cast AZS blocks, improper operation, such as collision, falling, etc., may cause damage to the block body and produce hidden cracks. These hidden cracks may gradually expand during subsequent use, forming obvious cracks.
3.1 Strengthen thermal insulation measures
During the cooling process of the fused cast AZS blocks, the volume of the fused block expanded rapidly with the transformation of ZrO2 from the high temperature cubic crystal system to the low temperature monoclinic crystal system.
In order to prevent cracking of the product due to excessive thermal stress caused by rapid cooling. Therefore, thermal insulation measures should be strengthened during its crystallization process. Usually, the thermal insulation annealing of fused cast AZS blocks is to put the sand mold into the incubator and fill it with the thermal insulation medium. When casting, the melt is injected into the sand mold and then placed in the annealing area for natural annealing. During the operation, the temperature difference between the casting and the annealed thermal insulation medium should be minimized to slow down the cooling speed to avoid cracks and control the temperature of the product. In this way, fused cast AZS block products with uniform structure and improved high temperature performance can be obtained. In view of the uneven stress distribution of special-shaped blocks and super-wide and super-large fused cast AZS blocks, it is easy to form cracks. In actual production, we adopt targeted auxiliary measures. Using the live basket type, after injecting the melt, it is placed in a thousand incubators and finally buried in an appropriate insulation medium for thermal insulation annealing. The annealing speed is maintained at about 60 ° C/h. In this way, the crack trend of the fused cast AZS block is significantly reduced.


3.2 Adopt new casting process
With the acceleration of the technological progress of glass furnaces, most glass furnaces are developing in the direction of heat preservation and energy saving. Therefore, the appearance quality requirements for fused cast AZS blocks are getting higher and higher, and the adoption of new casting processes is only a matter of time. There are several development directions in the future:
a, the use of the whole resin sand mold
b. Implementation of vacuum casting. The overall resin sand mold makes the appearance quality of products on a new level. The casting size is accurate, the surface is smooth, the sand mold at room temperature fast hardening, has the good high temperature self-collapse performance, the vacuum casting process also achieves the casting size is accurate, the surface is smooth, no need to bond Lai sand can be reused to save money, so this process should be as far as possible to promote the use of and to make the continuous improvement.
Henan SNR Refractory Co., Ltd (SNR) is professional in producing high-quality Fused Cast AZS Blocks for glass furnaces. If you have any needs, please contact me! 
 zoe@snrefractory.com
zoe@snrefractory.com



