There are many enterprises in China that produce electric melting refractory materials for glass furnaces, and the product quality level and its price vary greatly. Many manufacturers have great space for improvement in appearance quality, composition design, casting process and dimensional accuracy.
The block quality of the glass furnace sidewall block will directly affect the life of the glass furnace sidewall, especially the crystal phase structure, glass phase content and processing accuracy of the block. Fused cast AZS blocks have a cold compressive strength greater than 350 MPa due to its dense structure and low porosity, but the tensile strength is only about 20 MPa. When subjected to thermal shock and uneven heating, the tensile stress caused by the temperature difference is too large and the volume changes too fast, and there are no pores for buffering, so it is very easy to burst and crack.
Therefore, we learned that the characteristics of fused cast AZS blocks and the precautions for use, such as thermal shock resistance and corrosion resistance, will directly affect the stability and durability of glass furnaces. It helps to prevent potential problems such as cracking, spalling or erosion of the block body, thus extending the life of the glass furnace.
1. Characteristics of fused cast AZS block
• Composition and Phase Composition:
The main chemical composition of fused cast AZS blocks is alumina (AL2O3) and zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), as well as a small amount of silicon dioxide (SiO2). The content of AL2O3 is 50% to 70%, the content of ZrO2 is 20% to 40%, and the rest is SiO2. The main mineral compositions are oblique zircon (ZrO2), corundum (α-AL2O3) and glassy phase.
According to the content of zirconium dioxide, fused cast AZS blocks can be divided into different materials, such as AZS-33 (containing 33% ZrO2), AZS-36 (containing 36% ZrO2), and AZS-41 (containing 41% ZrO2).
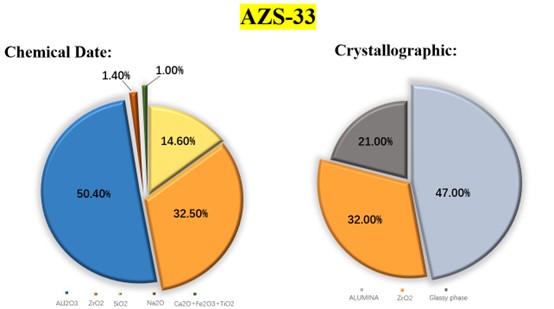
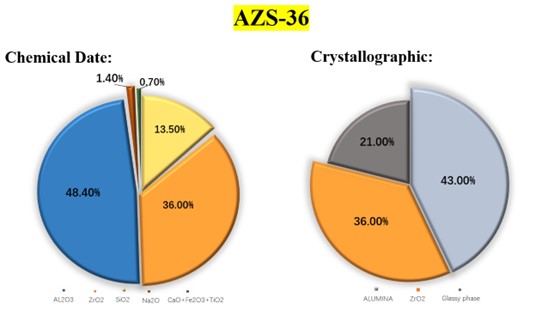
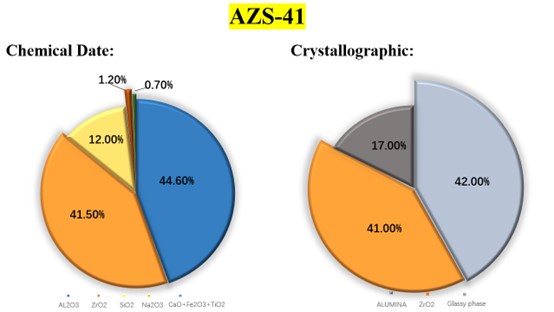
• Density and operating temperature
The density of fused cast AZS blocks is generally 3.4 to 4.0 g/cm ³, and its operating temperature is usually up to about 1700 ° C. However, in actual use, its performance will be affected by factors such as ZrO2 content: the higher the ZrO2 content, the density of fused cast AZS blocks will usually increase accordingly. For example, the density of fused cast AZS blocks containing 33% ZrO2 is about 3.45 to 3.6 g/cm ³; while the density of fused cast AZS blocks containing 41% ZrO2 will be slightly higher than this range.
Different production processes and equipment may also lead to certain differences in density. Advanced production processes can better control the melting, casting and cooling process of raw materials, so that the crystallization of blocks is denser, thereby increasing the density. In the actual glass furnace, the use temperature will also be restricted by environmental factors such as atmosphere, pressure, and impurity erosion in the glass furnace. For example, in the glass furnace, although the maximum use temperature of fused cast AZS blocks can reach about 1700 ° C, in the special case of strong alkaline or strong acidic medium erosion, it may be necessary to appropriately reduce the use temperature to ensure the service life of fused cast AZS blocks.
• Mechanical properties
Fused cast AZS blocks have high compressive strength at regular temperature, generally reaching hundreds of megapascals or even higher, which makes them less prone to deformation and damage when subjected to large static loads, and can ensure stable operation in various industrial equipment. In high temperature environments, fused cast AZS blocks can still maintain good strength properties. For example, in some high-temperature glass furnaces, when the temperature reaches 1000 ° C or more, its strength will decrease, but it can still be maintained at a certain level, which can effectively resist the impact and pressure of materials at high temperatures.
• Thermal characteristics
Irregular changes in thermal expansion: There is an abnormality in the expansion curve near 1000 ° C, and the internal ZrO2 crystals undergo reversible crystal transformation, resulting in large volume changes. Therefore, blocks containing ZrO2 are not suitable for use in parts with sharp temperature fluctuations around 1000 ° C. When baking a glass furnace, the temperature change at 900-1150 ° C should not be too large, generally not more than 15 ° C/h, and a smooth temperature increase is required.
• Anti-corrosion properties
Strong chemical resistance: ZrO₂ high melting point (2715°C), good chemical stability, strong corrosion resistance to acidic and alkaline media, especially glass liquid, can effectively resist the initialization and erosion of glass liquid, slag, etc., thus, ensuring the service life of the glass furnace. In high temperature aerobic environment, fused cast AZS blocks also have good oxidation resistance, which can form a dense oxide film on the surface to prevent oxygen from further invading the interior of the block body, thereby slowing down the oxidation reaction and protecting the block body from oxidation damage.


• Microstructural properties
The dense crystal structure: the internal crystal structure is closely arranged and the porosity is low, which makes the block body have good strength and anti-permeability, which can effectively prevent the intrusion of external substances and the loss of internal components.
• Good wear resistance
The surface of the fused cast AZS blocks are relatively smooth and has a low coefficient of friction, which helps to reduce the friction when it comes into contact with other objects and reduce the degree of wear. At the same time, its low coefficient of friction can also reduce the wear on other components used in conjunction with it, and improve the operating efficiency and reliability of the entire equipment. The wear resistance of the fused cast AZS blocks are mainly due to its dense crystal structure and high hardness. The crystal particles inside it are tightly bonded, and when subjected to wear, it is not prone to particle peeling and surface peeling, which can maintain good surface quality and dimensional accuracy for a long time.
2. Precautions when heating up
During the heating process of fused cast AZS sidewall blocks in the glass furnace, When the temperature is between 0 and 1100 ℃, the sidewall block expands linearly with the increase of temperature, and the expansion is about 0.8%.
When the temperature is 1100-1200 ℃, the monoclinic ZrO₂ in the block body transforms into tetragonal ZrO₂, and with the change of volume, the block body shrinks, and the bus expansion rate decreases from about 0.8% to about 0.6%;
When the temperature rises above 1200 ℃, the sidewall blocks begin to expand again as the temperature rises.
When the temperature is below 1600 ° C, the overall expansion characteristics of the sidewall blocks are not large.
 In the process of heating up glass furnace, the larger tensile stress will appear in the non-thermal insulation area of the upper part of the sidewall block, near the cold surface of the block. And increase with the increase of temperature until the temperature stabilizes. When the cooling air starts to blow, the tensile stress of the block body has a short peak, so generally when the stress is small, that is, when the heating up glass furnace temperature is lower than 700 ° C, the number of cracks generated is relatively small. Because of the lower insulation, the stress in the longitudinal direction of the sidewall is larger than the component in the vertical and thickness directions of the sidewall, which often exceeds the tensile strength limit of the block. Therefore, during the process of heating up the glass furnace, the sidewall block generally has longitudinal cracks during a period of time after the cooling air is turned on and the glass furnace temperature is 950-1200 ° C. The cracks develop to the thickness and vertical direction of the block. When the glass furnace temperature is 900-1200 ° C, the heating speed should not be too fast, and generally it is required not to exceed 15 ° C/h. When the internal temperature of the block body is greater than 1000 ° C, the block body can fully absorb the generated stress and cracks, and the cracks are also healed. The cracks generated by the kiln will not spread to the hot surface and thermal insulation area of the block.
In the process of heating up glass furnace, the larger tensile stress will appear in the non-thermal insulation area of the upper part of the sidewall block, near the cold surface of the block. And increase with the increase of temperature until the temperature stabilizes. When the cooling air starts to blow, the tensile stress of the block body has a short peak, so generally when the stress is small, that is, when the heating up glass furnace temperature is lower than 700 ° C, the number of cracks generated is relatively small. Because of the lower insulation, the stress in the longitudinal direction of the sidewall is larger than the component in the vertical and thickness directions of the sidewall, which often exceeds the tensile strength limit of the block. Therefore, during the process of heating up the glass furnace, the sidewall block generally has longitudinal cracks during a period of time after the cooling air is turned on and the glass furnace temperature is 950-1200 ° C. The cracks develop to the thickness and vertical direction of the block. When the glass furnace temperature is 900-1200 ° C, the heating speed should not be too fast, and generally it is required not to exceed 15 ° C/h. When the internal temperature of the block body is greater than 1000 ° C, the block body can fully absorb the generated stress and cracks, and the cracks are also healed. The cracks generated by the kiln will not spread to the hot surface and thermal insulation area of the block.
3. Summary
Due to the design and block laying reasons, the reserved expansion joints between the sidewall blocks or the partial position joints are not close, the heat is dissipated at the straight joints during the baking process, the temperature of the block edge rises, the tensile stress moves from the outer surface of the block to the inside, and the stress is changed, that is, there is a risk of horizontal cracks. Therefore, the pre-arrangement and precision machining of the sidewall blocks are also very important:
Heating speed: In the temperature range of 900 to 1200 ° C, the heating speed should not be too fast, generally not more than 15 ° C/h. This is because in this temperature range, the ZrO2 crystal inside the fused cast AZS sidewall block will undergo a transition from a monoclinic to a tetragonal crystal system, accompanied by a large volume change. If the temperature rises too fast, it may cause the block to burst.
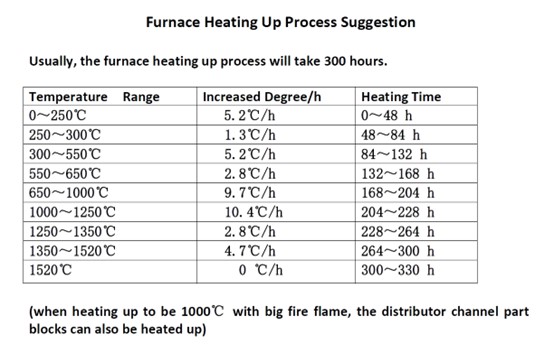
Temperature stability: When heating up a glass furnace, especially in the temperature range of 900 to 1150 ℃, the temperature change should not be too large, and it is necessary to maintain a steady temperature rise to prevent the block body from cracking due to uneven thermal expansion and contraction.
►Stress management
Tensile stress: During the heating up glass furnace process, the greater tensile stress occurs in the non-thermal insulation area on the upper part of the sidewall block, near the cold surface of the block, and increases with the increase of temperature. Therefore, it is necessary to pay close attention to the stress changes in these areas during the heating process to prevent the block body from bursting.
Cooling air: When the cooling air starts to blow, the tensile stress of the block body will have a short peak. Therefore, when the stress is small, that is, when the glass furnace’s temperature is lower than 700 ° C, the air is gradually added to reduce the generation of cracks.
►Fused cast AZS block protection
Reserved expansion joints: Since the fused cast AZS sidewall blocks will expand during the heating process, it is necessary to reserve enough expansion joints when laying blocks to prevent the blocks from squeezing each other due to expansion.
To prevent cold air from blowing directly: Avoid cold air blowing directly to certain parts, because if these parts are blown directly by cold air, they may burst, so other blocks are required to protect them. This is usually in a specific scene, which may be some parts that are more sensitive to temperature or easily damaged by cold air. By setting other blocks as a barrier to block the direct effect of cold air, it can play a protective role and prevent the occurrence of bursting.

►Material selection and matching
Avoid eutectic: Some refractory materials such as fused cast AZS sidewall blocks and clay bricks will have eutectic phenomenon at high temperature, resulting in a decrease in block performance. Therefore, when selecting refractory materials, it is necessary to avoid contacting two refractory materials with serious eutectic phenomenon.
Material purity: The purity of fused cast AZS sidewall block has an important impact on its performance. If the block contains too much impurities, it may affect its corrosion resistance and thermal expansion properties. Therefore, when choosing fused cast AZS block materials, it is necessary to pay attention to its purity.
Henan SNR Refractory Co., Ltd. is dedicated to the manufacturing and research and development of fused cast AZS refractory materials for the glass industry. Meanwhile, SNR can provide total solutions and services for glass furnace design, glass furnace construction, renovation and upgrading. Please contact me if you have any requirement.





